Palmoplantar Psoriasis
Palmoplantar Psoriasis
Understanding Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment of Psoriasis on the Hands and Feet
Introduction
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. One specific type of psoriasis is palmoplantar psoriasis, which primarily affects the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. This form of psoriasis can cause discomfort and interfere with daily activities. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of palmoplantar psoriasis, including its symptoms, causes, triggers, and available treatment options.
I. Understanding Palmoplantar Psoriasis
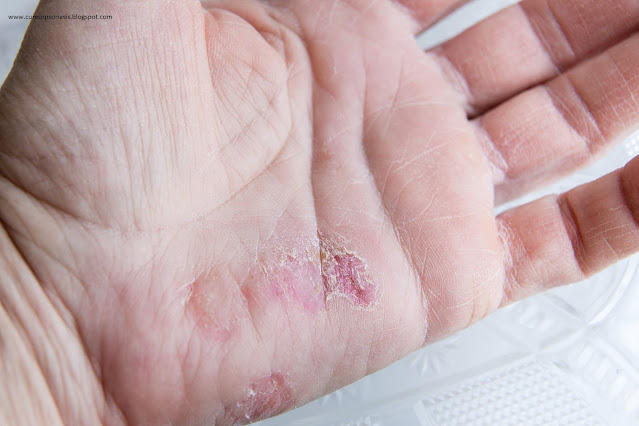
Palmoplantar psoriasis is a localized form of psoriasis that affects the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. It is characterized by the development of red, scaly patches in these areas. The skin may become thick, dry, and cracked, leading to pain, tenderness, and even difficulty in performing tasks that involve the hands or feet.
Palmoplantar psoriasis can occur in different patterns, including:
1. Palmar-Plantar Pustulosis (PPP): PPP is a variant of palmoplantar psoriasis that involves the formation of small, pus-filled blisters on the palms and soles. These blisters can be painful and may lead to the formation of crusts or scales.
2. Hyperkeratotic Palmoplantar Psoriasis: This pattern is characterized by the development of thickened, callus-like patches on the palms and soles. The skin may become extremely dry, flaky, and prone to cracking.
II. Symptoms of Palmoplantar Psoriasis
The symptoms of palmoplantar psoriasis can vary from person to person but commonly include:
1. Redness: Affected areas of the palms and soles may appear red or pink.
2. Scaling: The skin may develop thick, silvery-white scales that can be easily seen.
3. Dryness and Cracking: The skin may become excessively dry and prone to cracking, leading to pain and discomfort.
4. Itching and Burning: Palmoplantar psoriasis can cause itching and a burning sensation in the affected areas.
5. Pain and Tenderness: The thickened skin and cracks can be painful, especially when walking or using the hands.
III. Causes and Triggers of Palmoplantar Psoriasis
The exact cause of palmoplantar psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Potential triggers for palmoplantar psoriasis include:
1. Genetic Predisposition: People with a family history of psoriasis are more likely to develop palmoplantar psoriasis.
2. Immune System Dysfunction: Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to the symptoms of psoriasis.
3. Trauma or Injury to the Skin: In some cases, palmoplantar psoriasis can be triggered by physical trauma or injury to the skin, such as excessive friction or pressure on the palms or soles.
4. Environmental Factors: Certain environmental factors, such as stress, smoking, alcohol consumption, and certain medications, may trigger or worsen palmoplantar psoriasis symptoms.
IV. Treatment Options for Palmoplantar Psoriasis
The treatment of palmoplantar psoriasis aims to alleviate symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve the quality of life for individuals affected by the condition. Treatment options may include:
1. Topical Treatments: Topical corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, calcineurin inhibitors, or tar preparations may be prescribed to reduce inflammation, relieve itching, and promote healing of the affected areas.
2. Moisturizers and Emollients: Regularly applying moisturizers or emollients can help hydrate the skin, reduce dryness, and alleviate discomfort associated with palmoplantar psoriasis.
3. Phototherapy: Light therapy, such as narrowband ultraviolet B (NB-UVB) or psoralen plus ultraviolet A (PUVA), may be used to treat palmoplantar psoriasis. Controlled exposure to specific wavelengths of light can help slow down the overactive immune response and reduce inflammation.
4. Systemic Medications: In severe or resistant cases, systemic medications, such as methotrexate, acitretin, cyclosporine, or biologic agents, may be prescribed to control inflammation and modulate the immune system.
5. Localized Treatments: In some instances, localized treatments such as intralesional corticosteroid injections or the use of occlusive dressings may be recommended for stubborn or persistent palmoplantar psoriasis patches.
6. Lifestyle Modifications: Making specific lifestyle changes, such as managing stress, maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding triggers, practicing good hand and foot hygiene, and wearing comfortable footwear, can complement medical treatments and help manage palmoplantar psoriasis symptoms.
Conclusion
Palmoplantar psoriasis is a specific type of psoriasis that affects the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. It can cause discomfort, and pain, and interfere with daily activities. While there is no cure for palmoplantar psoriasis, various treatment options are available to alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. It is crucial for individuals with palmoplantar psoriasis to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan. By following medical advice, practicing good skincare, and managing triggers, individuals with palmoplantar psoriasis can minimize inflammation, reduce discomfort, and achieve better long-term outcomes.


















Comments
Post a Comment